Transmetteurs de pression NB-IoT vs. 4G : quelle solution cellulaire correspond à vos besoins IIoT ?
Date de sortie : 20/12/2025
Table des matières
Le passage à la surveillance cellulaire dans le secteur industriel
À l'ère de Industrie 4.0, Le “ dernier kilomètre ” de la collecte de données demeure un défi majeur pour les opérateurs des secteurs pétrolier, gazier et de l'eau. Traditionnellement, la surveillance de la pression dans les pipelines éloignés ou les puits de pétrole dispersés nécessitait un câblage coûteux ou des réseaux locaux complexes, dépendants d'une passerelle, comme Zigbee ou LoRaWAN. Aujourd'hui, le paradigme a changé.
L'émergence de Transmetteurs de pression sans fil de type réseau cellulaire, comme le Sunmoon SM39PWB, Cette solution permet aux opérateurs de tirer parti de l'infrastructure télécom mondiale existante. En éliminant le besoin de passerelles et de répéteurs locaux, les installations peuvent adopter un modèle de déploiement “ prêt à l'emploi ”.
Cependant, une question fréquente se pose lors du processus de sélection : faut-il choisir la communication NB-IoT ou 4G LTE ?
NB-IoT vs. 4G : Comprendre les protocoles
Pour prendre une décision éclairée, les ingénieurs doivent comprendre les compromis entre ces deux technologies cellulaires prises en charge par le SM39PWB.
1. NB-IoT (IoT à bande étroite) : le champion de l’efficacité NB-IoT est un Réseau étendu à faible consommation (LPWAN) Cette technologie est conçue spécifiquement pour les appareils nécessitant la transmission de faibles quantités de données sur de longues périodes.
- Avantages : Optimisée au maximum pour la consommation d'énergie (prolongeant considérablement l'autonomie de la batterie), elle offre une pénétration supérieure (idéale pour les fosses souterraines, les regards ou à l'intérieur d'enceintes en béton).
- Idéal pour : Surveillance statique d'installations telles que des réservoirs d'eau, des canalisations municipales ou des parcs de stockage de réservoirs isolés, où la latence en temps réel est moins critique, mais la durée de vie de la batterie est primordiale.
2. 4G (CAT-1/CAT-M) : Le choix de la performance Les réseaux 4G ou LTE Cat-1 standard offrent une bande passante plus élevée et une latence plus faible que le NB-IoT.
- Avantages : Transmission de données plus rapide et basculement réseau fiable pour les équipements mobiles. Ceci garantit que les pics de pression critiques sont signalés au serveur cloud avec une latence minimale.
- Idéal pour : Infrastructures critiques nécessitant des mises à jour quasi en temps réel, ou zones géographiques où la couverture NB-IoT n'est pas encore entièrement déployée par les opérateurs locaux.
L'avantage du Sunmoon SM39PWB
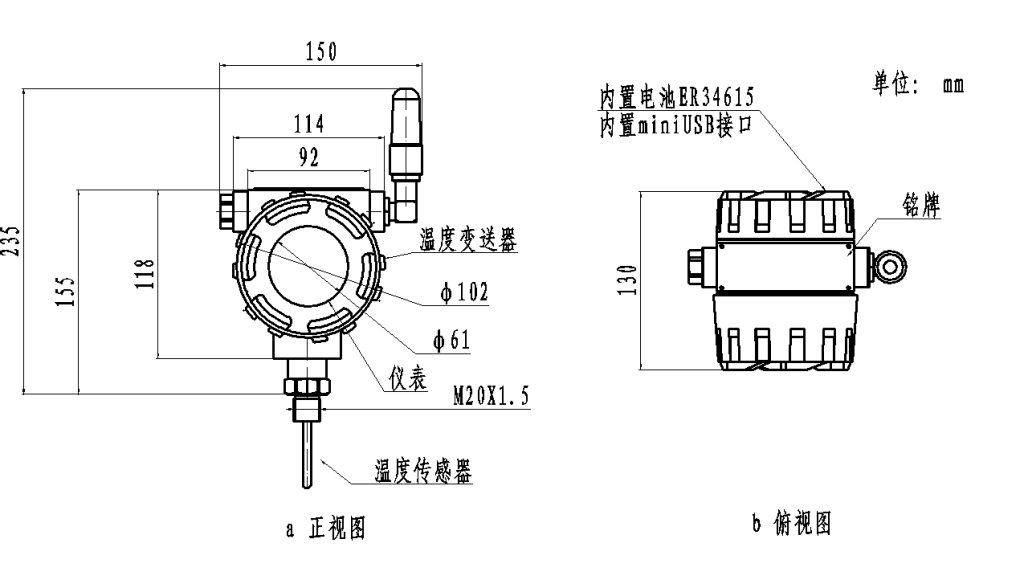
Le Émetteur de pression sans fil SM39PWB Conçu pour combler cet écart, le SM39PWB de Sunmoon Sensor (Riyue), fabricant spécialisé, est polyvalent. Que votre application exige la couverture étendue du NB-IoT ou l'omniprésence de la 4G, cet émetteur fournit des données précises avec une dérive de stabilité à long terme de seulement ±0,1% FS/an.
Les principaux avantages techniques sont les suivants :
- Coût d'infrastructure nul : Contrairement aux solutions RF propriétaires, le SM39PWB se connecte directement aux tours de télécommunications locales, réduisant considérablement les dépenses d'investissement initiales.
- Intégrité des données : Parmi ses fonctionnalités, on retrouve des fonctions de reprise après interruption et un stockage local des données, garantissant ainsi qu'aucune mesure n'est perdue lors de pannes réseau temporaires.
- Conception à faible consommation : Alimenté par une batterie haute capacité Batterie au chlorure de thionyle de lithium ER34615, L'appareil utilise des modes de veille intelligents pour maximiser sa durée de vie opérationnelle.

Conclusion
Le choix entre NB-IoT et 4G dépend de votre équilibre spécifique entre la granularité des données et la consommation d'énergie. Pour la plupart des applications de surveillance à distance statiques, le SM39PWB offre une solution robuste et économique qui réduit considérablement la consommation d'énergie. Coût total de possession (CTP) par rapport aux alternatives filaires.
Prêt à moderniser votre système de télémétrie ?
Contactez Sunmoon Sensor dès aujourd'hui pour discuter du protocole de communication le mieux adapté à vos conditions de terrain.


 />
/> />
/>